Structura cuptorului rotativ pentru industria cimentului și produse refractare Introducere
Cuptorul rotativ este un cilindru circular înclinat la un anumit unghi (3~5°) și căptușite cu materiale refractare. The diameter and length of the rotary kiln are related to the daily life of the rotary kiln.Production volume is directly related.
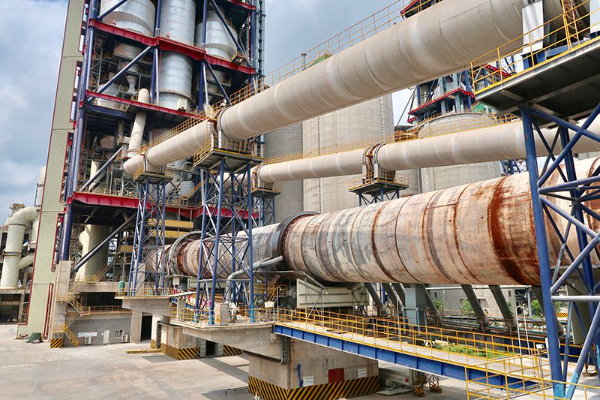

Rotary kiln operating structure
Cuptorul rotativ este un cilindru circular înclinat la un anumit unghi (3~5°) și căptușite cu materiale refractare. The diameter and length of the rotary kiln are related to the daily life of the rotary kiln.
Production volume is directly related.
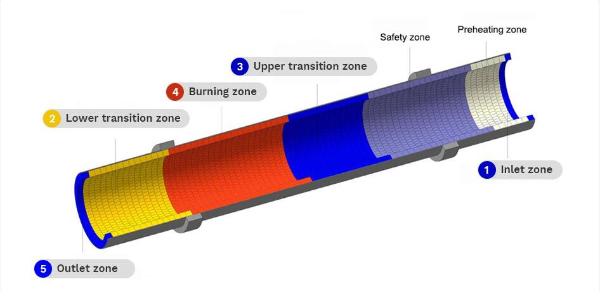
Decomposition zone
In the new dry process cement kiln, 90% of the raw material is decomposed in the pre-decomposition system outside the kiln, and the remaining 10% is completed in the decomposition zone in the rotary kiln, mainly the decomposition of calcium carbonate.
The material temperature in the decomposition zone is 800~1000°C, and the gas temperature is 1000~1400°C. The main environments faced by the refractory materials in the kiln are high temperature, chemical erosion such as alkali, sulfur, and chlorine, and mechanical stress caused by the rotation of the kiln body. Decomposition zone refractory materials need to have good mechanical strength and resistance to chemical attacks such as alkali.
The materials that can be used mainly include spinel bricks, anti-flaking high alumina bricks, silicon molybdenum bricks, and high alumina bricks.
Upper transition zone
Located behind the decomposition zone, the flue gas temperature in the kiln is approximately 1700°C. Affected by fuel combustion, the flue gas temperature changes frequently. The kiln skin in this area hangs and falls from time to time. The lining is in direct contact with the flue gas and clinker and is subjected to severe thermal stress. Changes frequently and is susceptible to clinker abrasion, high-temperature flue gas, and clinker
The erosion of coal-alkali sulfur compounds and the roundness stress of the cylinder in the wheel belt area.
The upper transition zone needs to withstand high-temperature impact and erosion from part of the cement clinker liquid phase, and it also needs to have good thermal strength.
Refractory bricks commonly include silica molybdenum bricks, magnesia-alumina spinel bricks, and special anti-flaking high alumina bricks.
Firing zone
In the highest temperature part of the kiln, the flame temperature can reach up to 1800~2000℃, and the kiln material temperature can reach 1350~1400℃. A large amount of cement clinker is formed. A stable kiln skin must be formed in this part to protect the lining bricks. în plus, a large amount of alkali and sulfur compounds in the kiln materials volatilize, so the lining bricks must have hanging kiln skins.
Performance, it can withstand the thermochemical erosion of melt components and alkali and sulfur compounds in the kiln skin, and it also needs to withstand the thermal shock stress and kiln damage caused by the collapse of the kiln skin.
The mechanical stress of the body rotation in the firing zone is high and the chemical reaction is violent. The refractory material is required to have good high-temperature resistance, alkali resistance, and cement clinker erosion. At the same time the refractory material here needs to be kiln-resistant to form a protective layer on the lining surface. În general, silica molybdenum bricks and periclase-spinel bricks are used.
lower transition zone
The kiln lining bricks in the lower transition zone bear the thermal stress of high-temperature air and clinker above 1400°C and are more capable of withstanding the stress of high-temperature dusty airflow and solidified clinker.
Abrasion, erosion from the melt in the clinker, sulfur and alkali compound melt and gas, deformation of the high-temperature cylinder, and ovality stress in the wheel belt.
The temperature in the lower transition zone is lower than that of the firing zone, and there is no stable kiln skin protection. The cement clinker is strongly eroded and eroded, and the temperature fluctuation range is large. Prin urmare, the refractory materials in this zone not only have the high refractoriness and high load of the refractory materials in the firing zone. In addition to softening temperature and high strength, it should also have good thermal shock resistance and kiln hanging performance. În general, silicon molybdenum red bricks and periclase-spinel bricks are used.
Cooling zone
The cooling zone of the new dry process cement rotary kiln is a similar area to the lower transition zone. The cement clinker cools and solidifies in this area and continues to move forward. It exits the kiln through the kiln mouth and enters the cooling system. In this area, the gas temperature is as high as 1400°C and the temperature fluctuates greatly. The grinding of clinker and the erosion of airflow are also very serious. The refractory material of the cooling zone needs to have wear resistance, alkali corrosion resistance, and good thermal shock resistance. Silica molybdenum bricks or anti-flaking high alumina bricks are usually used.
Front and rear kiln mouth
The rear kiln mouth is located at the connection between the pre-cliner kiln and the rotary kiln system. The temperature in the sub-region is relatively low, but it is subject to chemical erosion from the grinding of cement raw materials and the alkali and sulfur compounds circulated and enriched in the kiln; the front kiln mouth is located in the rotary kiln. At the discharging position, the temperature fluctuates greatly and the clinker and airflow erosion is relatively serious, which requires high wear resistance, thermal shock stability, and spalling resistance of the material.
The refractory materials at the front and rear kiln entrances need to have good wear resistance, alkali resistance, and spalling resistance. Corindon, corundum-mullite, mullite-silicon carbide castables, high-aluminum refractory castables, etc. are often used.

Coal injection pipe
The coal-injection pipe is a pipe that directly transports fuel and air to provide heat. The front end of the coal injection pipe is directly affected by the thermal radiation of the high-temperature flame and the grinding and erosion of cement clinker and airflow. Since modern rotary kilns also co-process solid waste and domestic garbage, Hazardous compounds such as alkali, sulfur, and chlorine seriously corrode coal injection pipe materials. Coupled with the thermal shock effects caused by temperature fluctuations, refractory materials must have good resistance to chemical erosion and thermal shock spalling.
Depending on the material usage environment, coal injection pipes mostly use corundum-mullite castables, steel fiber reinforced castables, low-cement high-aluminum castables, etc.
Tertiary air duct
The tertiary air duct is a hot air duct connecting the cooler and the pre-cliner kiln. It is used to transport the cement clinker waste heat to the pre-calciner kiln for reuse. The working environment of tertiary air ducts is harsh, especially at elbows and closing valves. The high-temperature airflow carries a large amount of dust and alkali, sulfur, and chlorine compounds, which wear and erodes the material, causing the material to become loose and peeling.
The tertiary air duct materials mainly consider wear resistance, alkali erosion resistance, and spalling resistance. Cărămizi rezistente la alcalii de înaltă rezistență, high-strength alkali-resistant castables, anti-crushing castables, etc. can be used.
What refractory materials are used in cement rotary kilns?

| Rotary kiln parts | Materiale refractare |
| Decomposition zone | Spinel bricks, anti-flaking high alumina bricks, silicon molybdenum bricks and high alumina bricks, etc. |
| Upper transition zone | Silicon molybdenum bricks, magnesia-alumina spinel bricks, and special anti-flaking high alumina bricks, etc. |
| Firing zone | Spinel bricks, anti-flaking high alumina bricks, silicon molybdenum bricks high alumina bricks, etc. |
| Lower transition zone | Silica molybdenum red bricks and periclase-spinel bricks, etc. |
| cooling zone | Silicon molybdenum bricks or anti-flaking high alumina bricks, etc. |
| Front and rear kiln mouth | Corindon, mullite-SiC castables, etc. |
| Coal injection pipe | Corundum-mullite castables, steel fiber reinforced castables, low cement castables, etc. |
| Tertiary air duct | Cărămizi rezistente la alcalii de înaltă rezistență, high-strength alkali-resistant castables, anti-crushing castables, etc. |
 Fabrica de refractare Rongsheng
Fabrica de refractare Rongsheng
WeChat
Scanați codul QR cu wechat