Principles of Blast Furnace Ironmaking Introduction
The blast furnace is an important metallurgical equipment used for iron-making. The principle of blast Furnace ironmaking converts iron ore into liquid iron and slag through the process of high-temperature reduction and melting, realizing the smelting process from ore to metal.

What are the methods of making iron?
Ironmaking methods mainly include the blast furnace method, direct reduction method, smelting reduction method, enz. The principle is that the ore obtains reduced pig iron through physical and chemical reactions in a specific atmosphere (reducing substances CO, H2, C; suitable temperature, enz.). Except for a small part of pig iron used in casting, most of it is used as raw material for steelmaking. Blast furnace ironmaking is the main method of modern ironmaking and an important link in steel production. This method was developed and improved from ancient shaft furnace ironmaking. The iron produced by blast furnaces accounts for more than 95% of the world’s total iron production. There are also many requirements for the vuurvaste materialen used in external blast furnaces. Neem contact met ons op voor meer informatie.
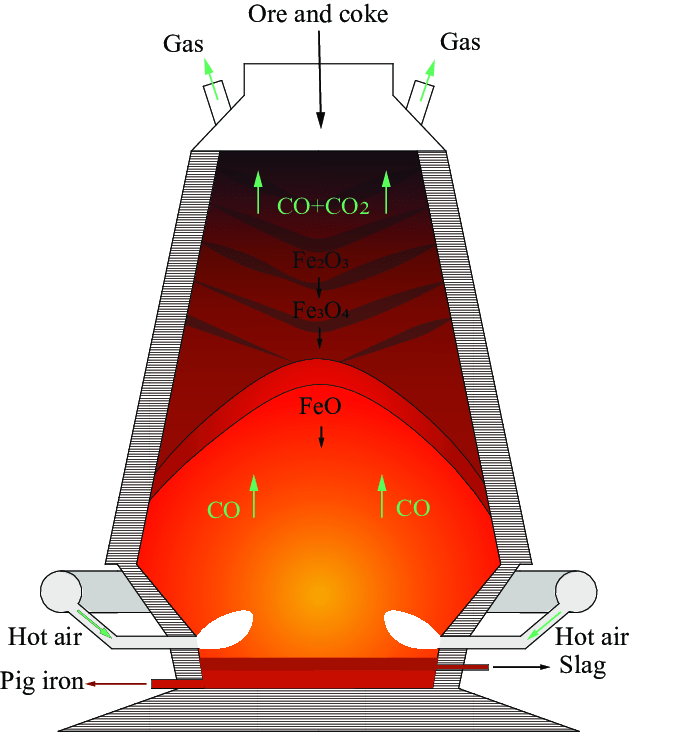
Introduction to blast furnace ironmaking process
The ironmaking process is to load iron-containing raw materials (sinter, pellets, or iron ore), fuel (coke, coal powder, enz.), and other auxiliary raw materials (limestone, dolomiet, manganese ore, enz.) from the top of the blast furnace in a certain proportion. into the blast furnace, and the hot blast furnace blows hot air into the blast furnace along the tuyere around the furnace to assist the coke combustion (some blast furnaces also inject auxiliary fuels such as pulverized coal, heavy oil, natural gas, enz.)
At high temperatures, the carbon in the Coke burns with oxygen blown into the air to produce carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Raw materials and fuels decline as the smelting process in the furnace proceeds. When the descending charge and the rising gas meet, heat transfer, afname, melting, and decarburization occur successively to generate pig iron.

The impurities in the iron ore raw materials are combined with the flux added into the furnace to form slag. The molten iron at the bottom of the furnace is intermittently released into a molten iron tank and sent to the steelmaking plant.
The impurities in the iron ore raw materials are combined with the flux added into the furnace to form slag. The molten iron at the bottom of the furnace is intermittently released into a molten iron tank and sent to the steelmaking plant.
 Rongsheng Vuurvaste Fabriek
Rongsheng Vuurvaste Fabriek
WeChat
Scan de QR-code met wechat