Αιτίες και αντίμετρα από χυτοσίδηρο βλάβης του κονιορτοποιημένου καυστήρα άνθρακα στον περιστροφικό κλιβάνου τσιμέντου
In modern new dry process cement production lines, the system equipment is constantly increasing, the output of cement clinker has doubled, the load on the refractory materials used in the system is also increasing, and the use conditions are becoming more and more harsh. Only high-performance refractory materials can ensure the normal operation of production equipment. The castables in the burner area are subjected to the violent erosion of high-temperature dusty airflow, and the temperature in this area changes dramatically. The concentration of alkali vapor in the gas is high, and the castables are prone to cracking and peeling, resulting in a serious reduction in service life.
Damage to castable material at burner
Normally, the χυτά of the burner will be damaged to varying degrees after working for 3 να 4 months. Under the action of thermal stress and mechanical stress, the micro cracks in the castables continue to expand and extend, resulting in castable peeling. The following is an analysis of the causes of thermal stress and mechanical stress.
1. Effect of thermal stress
The rotary kiln burner is located at the front kiln mouth, and the working environment temperature is about 600℃~1300℃, which is high and has a wide fluctuation range. Since the pulverized coal burner castable is a poor conductor of heat, the temperature difference leads to different thermal expansion coefficients, and cracks will appear in the unevenly heated parts after a period of use.
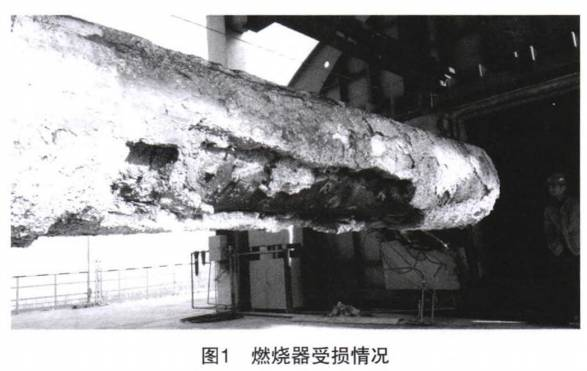
Εξάλλου, horizontal construction is adopted during the castable construction process. Due to the effect of gravity, there will inevitably be differences between the castables in the upper and lower parts of the cylinder. The different densities lead to uneven heat conduction and are prone to cracks.

2. Effects of mechanical stress
High-temperature secondary air is blown into the rotary kiln from the bottom of the pulverized coal burner by the grate cooler. This part of the secondary air carries more or less clinker dust, which causes great erosion to the lower part of the pulverized coal burner. This causes the cracks to gradually grow larger, and even expose the internal anchors. The welding parts of the anchors will be melted under high temperature, and the anchors will fall together with the castables due to gravity, exposing the metal shell of the burner. Without the protection of the castables, the burner is prone to cracks at high temperatures. Once cracks occur and air leakage occurs, the burner cannot be used anymore.

Countermeasures for castable damage of pulverized coal burner
1. Castable construction method
Due to the limited on-site construction conditions, horizontal construction of castables has the advantages of convenience, speed and cost savings, so it is adopted by most construction units. Ωστόσο, due to gravity, the horizontally constructed castables will definitely have different degrees of uneven density up and down, and will be more likely to deform and fall off in the rotary kiln. Επομένως, it is recommended to use vertical construction, which means using lifting equipment to lift the entire burner vertically to the ground for pouring. This pouring method can make the density of the castable more uniform and the head pouring more tightly. Construction method
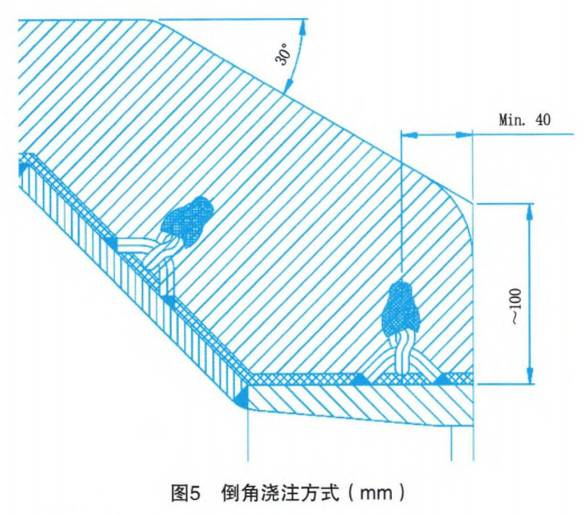
2. The shape of the burner head casting material is chamfered

In the airflow inside the rotary kiln, the outer side of the primary air generated by the pulverized coal burner is prone to generate vortex flow, and the airflow will drive some pulverized coal to adhere to the head of the pulverized coal burner, resulting in coking. As the coking gradually increases and spreads, it interferes with the flame shape, resulting in uneven temperature on both sides of the burner. Επομένως, the pulverized coal burner cannot be simply cast into a barrel shape. Figure 4 shows a simple barrel shape. αντι αυτου, it should be cast into a chamfer (recommended 30°~40°). The chamfer casting method can simply and effectively reduce the coking phenomenon.
3. Anchor arrangement
All anchors are welded in a vertical alternating manner with a distance of 150mm. Γενικά, manufacturers will add plastic caps to anchors. If the plastic caps are lost, they will be replaced with a layer of asphalt. They should not be in direct contact with the castable. Before pouring, all anchors and all surfaces should be waxed to prevent the castable from being damaged by the thermal expansion of the burner.
4. Selection and proportioning of castables
The castable is selected according to the principle of high temperature wear resistance, spalling resistance, and relatively small weight (the weight of the cantilever pulverized coal burner is strictly controlled). Because the lower front end of the pulverized coal burner castable is very easy to wear, it is recommended to add SiC or other high temperature wear-resistant materials. Strictly control the amount of water used in construction. It is recommended that the water consumption be less than 8%, depending on the specific requirements of the refractory model used. Under the premise of ensuring the construction performance, the amount of water added should be strictly controlled, and it is better to be less rather than more.
5. Expansion joint retention
An expansion joint should be left every 1m in the circumferential direction of the pulverized coal burner castable, και 2 να 4 expansion joints should be left in the axial direction (staggered joints). The width of the expansion joint is 10mm, and the expansion joint is filled with ceramic fiber blanket.
 Rongsheng Refractories Factory
Rongsheng Refractories Factory
WeChat
Σαρώστε τον κωδικό QR με το wechat