Commonly used carbon refractory materials for blast furnaces
The carbon refractory materials commonly used in blast furnaces mainly include carbon bricks, graphite carbon bricks, graphite silicon carbide bricks, self-bonded or nitrogen-bonded silicon carbide bricks and ramming materials.
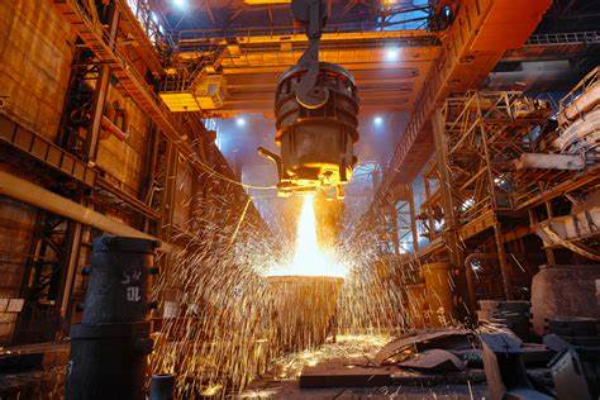

Advantages of carbon refractory materials for blast furnaces
① High refractoriness (carbon sublimates at 350C), it neither melts nor softens at blast furnace temperature.
② Small thermal expansion coefficient, good volume stability in a wide temperature range.
③ Carbon-saturated molten iron does not wet carbon bricks, and under certain cooling conditions, slag has little erosion on the carbonaceous furnace lining.
④ It has high thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. It can fully exert the efficiency of the cooler when used in the furnace bottom and furnace hearth, thereby extending the service life of the furnace lining and preventing burn-through.
⑤ It has excellent cutting performance and can be made into special-shaped products with very small dimensional tolerances to meet masonry requirements.
Commonly used blast furnace carbon refractory materials
Silicon carbide bricks
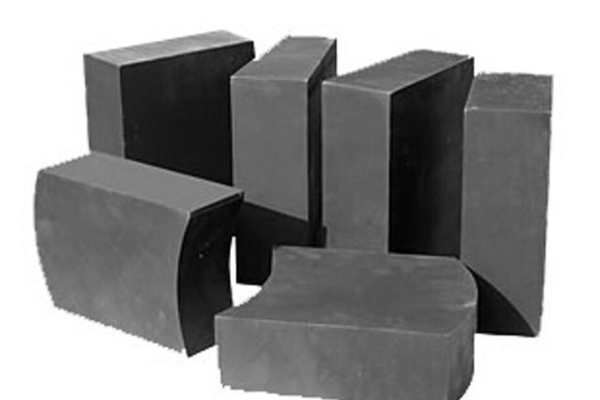

Silicon carbide bricks have good thermal conductivity, small expansion coefficient, high high temperature strength, small creep deformation, good resistance to slag, molten iron erosion and corrosion, and better oxidation resistance than carbonaceous materials. The main problem is to find a binder that resists alkali metal corrosion. There are also silicon carbide refractory materials bonded with nitrides or bonded with themselves. Silicon carbide bricks are preferred to extend the service life of the lower part of the furnace body.
Aluminum carbon brick
Aluminum carbon bricks for blast furnaces are made of high-quality high-alumina bauxite and graphite as the main raw materials, with a small amount of silicon carbide and additives added, and resin as a binder. After being pressed and formed, they are solidified and baked to form products. It has the characteristics of high-temperature resistance, good thermal conductivity, good alkali resistance, low porosity, small deviation of external dimensions, and low price. It can be used in blast furnace bosh, furnace waist, furnace body, iron mouth area, furnace bottom top layer, and other parts.
Monolithic refractory materials
Compared with shaped refractory materials, monolithic refractory materials have a simple manufacturing process, convenient use, and plasticity. They are easy to form complex products and are conducive to the mechanization of furnace construction. They are low in cost and have a service life similar to that of refractory bricks. Their refractoriness and chemical stability are close to or reach the level of similar refractory bricks. They can be prefabricated into large blocks, but they must be strictly baked when used, especially at low temperatures, which takes a long time, and the strength at medium temperatures is low. They are easy to peel off when used for a long time at high temperatures.

 Rongsheng Refractories Factory
Rongsheng Refractories Factory
WeChat
Scan the QR Code with wechat